Understanding the P/E Ratio
May 18, 2024 By Susan Kelly
In the world of investment analysis, the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio is a crucial measure. This ratio provides an understanding of how much a company's stock is valued compared to its earnings. It shows what investors are ready to pay for each dollar earned by that company. By understanding the P/E ratio, investors can use this information to make decisions regarding buying stocks. They take into account factors like growth chance and market feeling.
Interpreting the P/E Ratio
Understanding the P/E ratio involves interpreting what it signifies. If the P/E ratio is high, this could mean investors expect more earnings growth in upcoming times. On the other hand, a low P/E ratio might imply underestimation or doubt about a company's potential for expansion. However, it is important to keep in mind industry standards and compare the P/E ratio of a company with its competitors for a more complete comprehension.

It is also significant to understand that the P/E ratio can differ greatly from one industry to another because of varying growth rates, risk characteristics, and capital setups. For instance, in the tech sector you usually see bigger P/E ratios because these firms have more chance for quick expansion; on the other hand utility businesses often show smaller P/E ratios due to their steady but slower growth character.
- Consider Industry Norms: Compare the P/E ratio of a company with the average P/E ratio of its industry to assess its relative valuation within its sector.
- Evaluate Growth Prospects: Analyze the company's growth prospects and future earnings potential to determine whether its current P/E ratio is justified.
Calculation of the P/E Ratio
The calculation of the P/E ratio is not complex. You can get it by dividing the market price per share through earnings per share (EPS). Market prices for each share may be found on financial websites or stock market platforms. EPS, however, is found by dividing the company's net income by its total number of outstanding shares. With this count, investors can gauge how appealing a stock is based on its earnings.
It is important to understand that the P/E ratio is a moving metric. As stock prices and earnings change, this ratio also changes. Therefore, investors should update their analysis often to consider current market conditions.
- Account for Dilution: Consider the impact of potential dilution from convertible securities or stock options when calculating EPS, as it can affect the accuracy of the P/E ratio.
- Adjust for Extraordinary Items: Exclude any extraordinary or one-time items from both the earnings and market price figures to ensure a more accurate assessment of the company's performance.
Significance in Investment Analysis
The P/E ratio, in the world of investment analysis, is like a main tool to see if stocks are good or not. It helps compare companies in similar industries or sectors so investors can spot stocks that might be undervalued or overvalued. Changes in the P/E ratio over time could show us changes in people's feelings towards the market, economic situations, and how well a company is doing. Thus, incorporating the P/E ratio into investment strategies can enhance decision-making processes.
Another important point to think about is how the P/E ratio relates to the growth rate of a company. A company that has high growth might deserve a higher P/E ratio than one with slower growth because it shows what earnings investors expect in the future.
- Assess Market Sentiment: Monitor changes in the P/E ratio over time to gauge shifts in investor sentiment towards the stock or the overall market.
- Consider Long-Term Trends: Evaluate the historical trend of the company's P/E ratio to identify patterns or anomalies that may inform investment decisions.
Limitations of the P/E Ratio
The P/E ratio gives a useful understanding, but it also has limitations. Its main problem is relying on earnings which could be changed or unstable. The P/E ratio might not include special events that could affect earnings and happen only once. In addition, comparisons may be impacted by variations in accounting approaches used by different companies. Hence, investors need to reinforce their evaluations with additional measurements along with qualitative elements.
When comparing P/E ratios, investors must use care especially if they are looking at businesses in various industries. The kind of business each company has might need different ways to value it. Also, only using the P/E ratio for making investment choices and not thinking about other things such as how much growth is possible, industry changes, or general economic situations could cause less than ideal results.
- Consider Industry Dynamics: Recognize that certain industries may have inherently higher or lower P/E ratios due to their unique characteristics, such as growth potential, regulatory environment, or market demand.
- Evaluate Earnings Quality: Scrutinize the quality and sustainability of the company's earnings, as a high P/E ratio based on inflated or unsustainable earnings may indicate a potential risk of overvaluation.
Variations and Adjustments
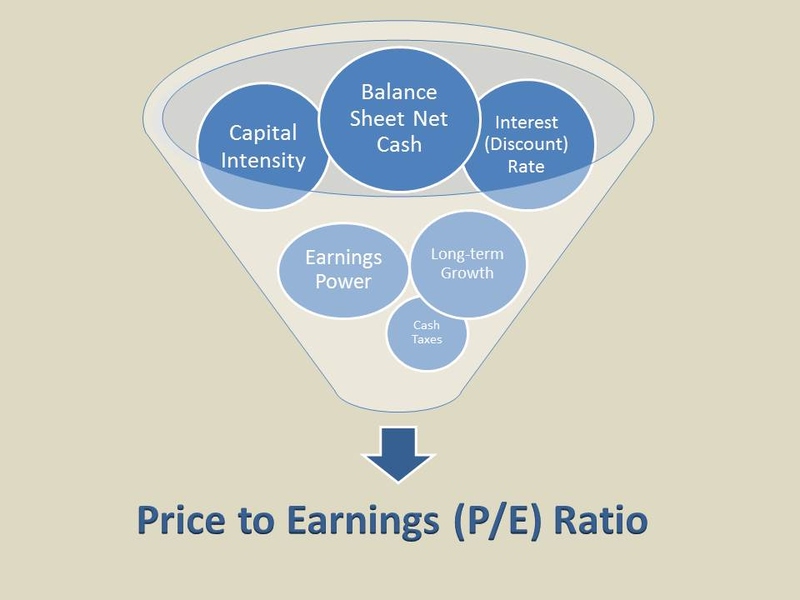
Different variations of the P/E ratio are used in practical applications to align with specific factors. For example, the forward price/earnings ratio incorporates anticipated earnings in place of past earnings. This change offers a view into what lies ahead, which is particularly beneficial for businesses that are growing rapidly or going through changes. Also, changes to the P/E ratio, like not including exceptional items or one-time costs, might give a more precise illustration of how much money the company can make.
Secondly, the P/E ratio for trailing twelve months (TTM) is another method that investors could consider. This uses the company's most recent twelve months of earnings data, taking into account how earnings have changed over time and giving a more up-to-date evaluation of valuation. Additionally, there exist variations like the price-to-earnings-to-growth (PEG) ratio which includes earnings growth in the analysis providing a broader perspective on valuation compared to growth potential.
- Consider Future Expectations: Utilize the forward P/E ratio to incorporate analysts' earnings forecasts and assess the company's valuation based on expected future performance.
- Account for Growth: Evaluate the PEG ratio to factor in the company's earnings growth rate and determine whether its valuation is justified relative to its growth prospects.
Conclusion
At the heart of investment analysis, the P/E ratio is a key tool that provides an understanding of stock valuation and market sentiment. By knowing its definition, interpretation, and calculation method, investors can make wise choices to enhance their investment portfolios. However, it's important to recognize its restrictions and use other metrics as well as non-quantitative evaluations. Understanding the P/E ratio helps investors to make wise and careful choices in the complex world of finance.








